テスト前のリスト導入の復習
前回のリスト構造の導入では、配列のデータに次のデータの入っている番号を添えることで途中にデータを挿入できるデータ構造の説明をした。
ヒープメモリとは
Javaでは、すべてのオブジェクトはヒープメモリに保存する。
ヒープメモリとは、一時的なデータの保管場所であり、new 演算子でデータを保存する場所を確保する。
Javaでは、分かり難いのでC言語で説明を行う。malloc() は、指定されたバイト数のメモリをヒープ領域に確保する命令。malloc() に失敗すると、NULL が返ってくる。また、使い終わったら malloc() の領域は free() 命令で返却が必要となる。
((( 配列をヒープメモリで確保 )))
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int a[ 5 ] = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 } ;
int* b ;
if ( (b = (int*)malloc( sizeof( int ) * 5 )) != NULL ) {
for( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++ )
b[ i ] = i + 1 ;
free( b ) ; // malloc() で確保したメモリ領域は返却が必要
}
return 0 ;
}
((( オブジェクトをヒープメモリに確保 )))
struct Complex {
double re ;
double im ;
} ;
int main() {
struct Complex* c ;
if ( (c = (struct Complex*)malloc( sizeof( struct Complex ) )) != NULL ) {
c->re = 1.23 ;
c->im = 2.34 ;
free( c ) ;
return 0 ;
} else {
printf( "No heap memory\n" ) ;
return 1 ;
}
}
((( 上記C言語をJavaで書くと )))
class Complex {
double re ;
double im ;
Complex( double r , double i ) {
this.re = r ;
this.im = i ;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
try {
Complex c = new Complex( 1.23 , 2.34 ) ;
// Javaではヒープメモリが確保に失敗したら、
// OutOfMemoryErrorの例外が発生する。
c = null ; // free()はJavaでは不要
// nullを代入してもいい。
} catch( OutOfMemoryError e ) {
System.out.println( "No heap memory" ) ;
System.exit( 1 ) ;
}
}
}
リスト構造 ListNode
前述の data と next で次々とデータを続けて保存する方法を、next の部分を次のデータへの参照を用いるように、リスト構造(連結リスト)を定義する。
import java.util.*;
class ListNode {
int data ; // データ部分
ListNode next ; // 次のデータへの参照
// コンストラクタ
ListNode( int d , ListNode nx ) {
this.data = d ;
this.next = nx ;
}
} ;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
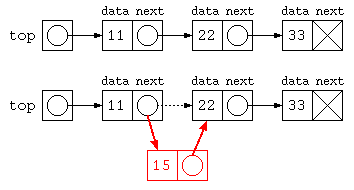
ListNode top = new ListNode( 11 , new ListNode( 22 , new ListNode( 33 , null ) ) ) ;
for( ListNode p = top ; p != null ; p = p.next )
System.out.println( p.data ) ;
// 途中にデータを入れる
top.next = new ListNode( 15 , top.next ) ;
for( ListNode p = top ; p != null ; p = p.next )
System.out.println( p.data ) ;
}
}
リスト操作
リスト構造に慣れるために簡単な練習をしてみよう。リスト構造のデータに対するメソッドをいくつか作ってみよう。print() や sum() を参考に、データ数を求める count() , 最大値を求める max() , データを検索する find() を完成させてみよう。
class ListNode {
(略)
} ;
public class Main {
static void print( ListNode p ) { // リストを表示
for( ; p != null ; p = p.next )
System.out.print( p.data + " " ) ;
System.out.println() ;
}
static int sum( ListNode p ) { // リストの合計を求める
int s = 0 ;
for( ; p != null ; p = p.next )
s += p.data ;
return s ;
}
static int count( ListNode p ) { // データ件数を数える
}
static int max( ListNode p ) { // データの最大値を求める
}
static boolean find( ListNode p , int key ) { // データ列の中から特定のデータを探す
// 見つかったら true , 見つからなければ false
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ListNode top = new ListNode( 11 , new ListNode( 22 , new ListNode( 33 , null ) ) ) ;
print( top ) ;
System.out.println( "合計:" + sum( top ) ) ;
System.out.println( "件数:" + count( top ) ) ;
System.out.println( "最大:" + max( top ) ) ;
System.out.println( "検索:" + (find( top , 22 )
? "みつかった" : "みつからない" ) ) ;
}
}
オブジェクト指向っぽく書いてみる
前述のプログラムでは、print( top ) のように使う static な関数としてプログラムを書いていた。しかし、オブジェクト指向であれば、オブジェクトに対するメソッドだと top.print() のように書きたい。この場合だと、以下のように書くかもしれない。
import java.util.*;
class ListNode {
int data ;
ListNode next ;
ListNode( int d , ListNode n ) {
this.data = d ;
this.next = n ;
}
void print() { // リストの全データを表示
for( ListNode p = this ; p != null ; p = p.next )
System.out.print( p.data + " " ) ;
System.out.println() ;
}
int sum() { // リストの合計を求める
int s = 0 ;
for( ListNode p = this ; p != null ; p = p.next )
s += p.data ;
return s ;
}
} ;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ListNode top = new ListNode( 11 , new ListNode( 22 , new ListNode( 33 , null ) ) ) ;
top.print() ;
System.out.println( "合計: " + top.sum() ) ;
ListNode list_empty = null ;
list_empty.print() ; // 実行時エラー java.lang.NullPointerException ぬるぽ!
}
}
しかし、データ件数 0件 に対してメソッドを呼び出せない。
ListNode と List というクラスで書いてみる
ひとつの方法として、リストの先頭だけのデータ構造を宣言する方法もある。
class ListNode {
int data ;
ListNode next ;
ListNode( int d , ListNode n ) {
this.data = d ;
this.next = n ;
}
} ;
class List {
ListNode top ;
List( ListNode p ) {
this.top = p ;
}
void print() {
for( ListNode p = top ; p != null ; p = p.next )
System.out.print( p.data + " " ) ;
System.out.println() ;
}
} ;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
List list = new List( new ListNode( 11 , new ListNode( 22 , new ListNode( 33 , null ) ) ) ) ;
list.print() ;
List list_empty = new List( null ) ;
list_empty.print() ;
}
}
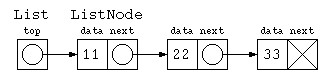
しかし、List と ListNode の2つのデータの型でプログラムを書くのは面倒くさい。
授業ではシンプルに説明したいので、今後はこの方法は極力避けていく。
先頭にダミーデータを入れる
複数のクラス宣言するぐらいなら、リストデータの先頭は必ずダミーにしておく方法もあるだろう。
import java.util.*;
class ListNode {
int data ;
ListNode next ;
ListNode( int d , ListNode n ) {
this.data = d ;
this.next = n ;
}
void print() { // リストの全データを表示
for( ListNode p = this.next ; p != null ; p = p.next )
System.out.print( p.data + " " ) ;
System.out.println() ;
}
} ;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ListNode list = new ListNode( -1 , null ) ;
list.next = new ListNode( 11 , new ListNode( 22 , new ListNode( 33 , null ) ) ) ;
top.print() ;
System.out.println( "合計: " + top.sum() ) ;
ListNode list_empty = new ListNode( -1 , null ) ;
list_empty.print() ;
}
}
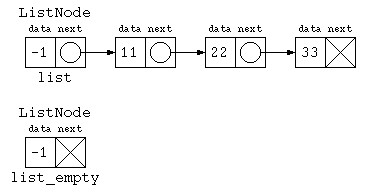
以降、必要に応じて、先頭にダミーを入れる手法も取り混ぜながらプログラムを書くこととする。
入力データをリストに追加
入力しながらデータをリストに格納する処理を考えてみる。
リストでデータを追加保存するのであれば、一番簡単なプログラムは、以下のように先頭にデータを入れていく方法だろう。
class ListNode {
(略)
void print() {
for( ListNode p = this ; p != null ; p = p.next )
System.out.print( p.data ) ;
System.out.println() ;
}
} ;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] inputs = { 11 , 22 , 33 } ;
ListNode top = null ;
for( int datum : inputs )
top = new ListNode( datum , top ) ;
top.print() ;
}
}
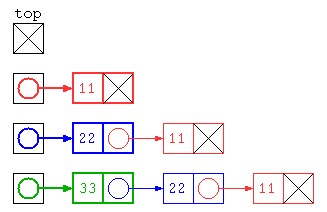
でもこの方法だと、先頭にデータを入れていくため、保存されたデータは逆順になってしまう。
末尾にデータを入れる
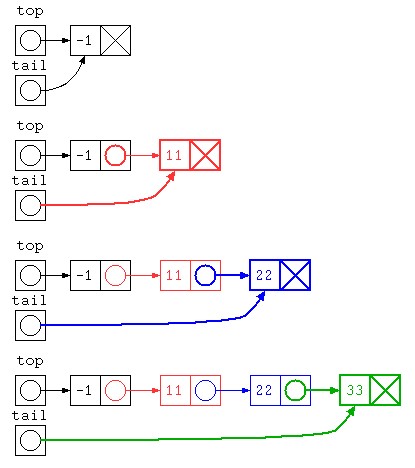
逆順になるのを避けるのであれば、データを末尾に追加する方法があるだろう。ただし初期状態でデータが0件だと処理が書きづらいので、先頭にダミーを入れておく方法で書いてみる。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] test_data = { 11 , 22 , 33 } ;
ListNode top = new ListNode( -1 , null ) ; // ダミー
ListNode tail = top ;
for( int x : test_data ) {
tail.next = new ListNode( x , null ) ;
tail = tail.next ;
}
top.print() ; // -1 11 22 33
} // ダミー
}