2分探索木にデータを追加
前回の2分探索木では、基本的な説明ということで、木の生成では直接木構造を生成していた。しかし、本来であれば、扱うデータに応じて木を生成することが求められる。
Javaの場合
以下の Javaのプログラムの関数 entry( … ) では、再帰を使いながら、value を追加した木を返す関数で記述した。
import java.util.*;
class BTreeNode {
int data ;
BTreeNode left ;
BTreeNode right ;
BTreeNode( int x , BTreeNode l , BTreeNode r ) {
this.data = x ;
this.left = l ;
this.right = r ;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void print_tree( BTreeNode p ) {
// 木構造をわかりやすくするために()をつけて表示
if ( p != null ) {
System.out.print( "(" ) ;
print_tree( p.left ) ;
System.out.print( p.data ) ;
print_tree( p.right ) ;
System.out.print( ")" ) ;
}
}
public static BTreeNode entry( BTreeNode p , int value ) {
if ( p == null ) {
return new BTreeNode( value , null , null ) ;
} else {
if ( p.data == value )
; // 何もしない
else if ( p.data > value )
p.left = entry( p.left , value ) ;
else
p.right = entry( p.right , value ) ;
return p ;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BTreeNode top = null ;
top = entry( top , 42 ) ;
top = entry( top , 27 ) ;
top = entry( top , 72 ) ;
top = entry( top , 13 ) ;
top = entry( top , 38 ) ;
top = entry( top , 64 ) ;
top = entry( top , 81 ) ;
print_tree( top ) ; System.out.println() ;
}
}
// 動作結果
// (((13)27(38))42((64)72(81)))
- 2分探索木へのデータの追加(Paiza.io)
しかしながらこのプログラムでは、以下のように小さい順序でデータを与えると、右に伸びる木が作られてしまう。
// 不均一な木ができる場合
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BTreeNode top = null ;
top = entry( top , 13 ) ;
top = entry( top , 27 ) ;
top = entry( top , 38 ) ;
top = entry( top , 42 ) ;
top = entry( top , 64 ) ;
top = entry( top , 72 ) ;
top = entry( top , 81 ) ;
print_tree( top ) ; System.out.println() ;
}
// 動作結果
// (13(27(38(42(64(72(81)))))))
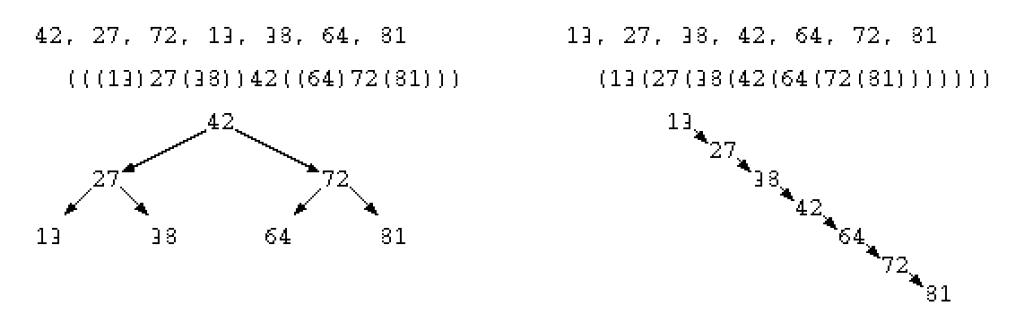
このような不均一な木が生成されてしまうと、本来であればデータ探索の処理時間は O( log N ) であるが、最悪の状態では O( N ) となってしまう。
AVL木
こういった偏った木が生成されてしまった時には、以下のような処理を加えると、不均一な状態を改善できる。
depth() 関数は与えられた木の深さを求める関数であり、左枝と右枝が大きく違う場所で 木の右回転を行う rotate_right() を実行する。
public class Main {
public static int depth( BTreeNode p ) { // 木の深さを求める
if ( p == null ) {
return 0 ;
} else {
int l = depth( p.left ) ;
int r = depth( p.right ) ;
if ( l > r )
return 1 + l ;
else
return 1 + r ;
}
}
public static BTreeNode rotate_right( BTreeNode p ) {
BTreeNode q = p.left ; // p
BTreeNode r = q.right ; // / \
q.right = p ; // q
p.left = r ; // / \
return q ; // r
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BTreeNode top = null ;
top = entry( top , 86 ) ;
top = entry( top , 53 ) ;
top = entry( top , 92 ) ;
top = entry( top , 11 ) ;
top = entry( top , 65 ) ;
top = entry( top , 22 ) ;
// 不均一な状態を確認
print_tree( top ) ;
System.out.println() ;
System.out.println( "p.left=" + depth( top.left ) ) ;
System.out.println( "p.right=" + depth( top.right ) ) ;
// top の右回転を実行
top = rotate_right( top ) ;
// 改善された状態を確認
print_tree( top ) ;
System.out.println() ;
System.out.println( "p.left=" + depth( top.left ) ) ;
System.out.println( "p.right=" + depth( top.right ) ) ;
}
}
- AVL木と右回転(Paiza.io)
上記のプログラムでは、左枝が3段で右枝が1段であり不均一な状態となっている。
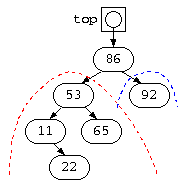
そこで、最上段の86の左枝を上に移動させるように枝の繋ぎ方を rotate_right() により変更している。実際には、繋ぎ変えを左回転させる処理も作る必要がある。
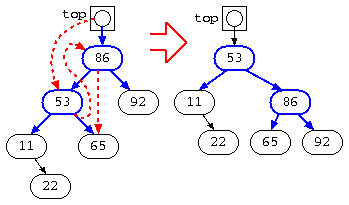 このように、木の枝の深さが不均一な場所で、このような処理を加えて均一化を図った木構造は AVL 木と呼ぶ。
このように、木の枝の深さが不均一な場所で、このような処理を加えて均一化を図った木構造は AVL 木と呼ぶ。
AVL木は、考案した Velski と Landis の名前が由来(Adelson-Velskii and Landis’ tree)